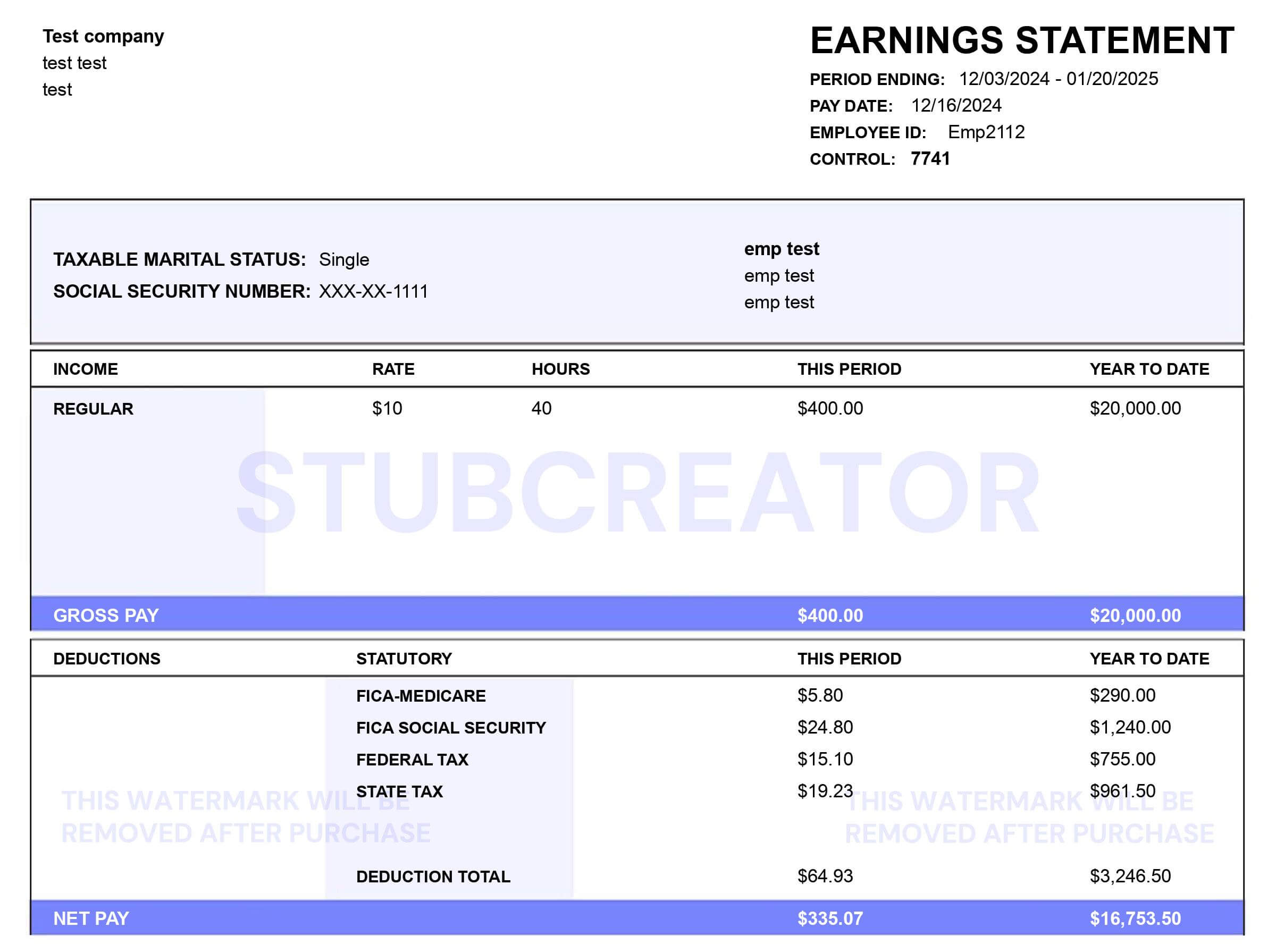
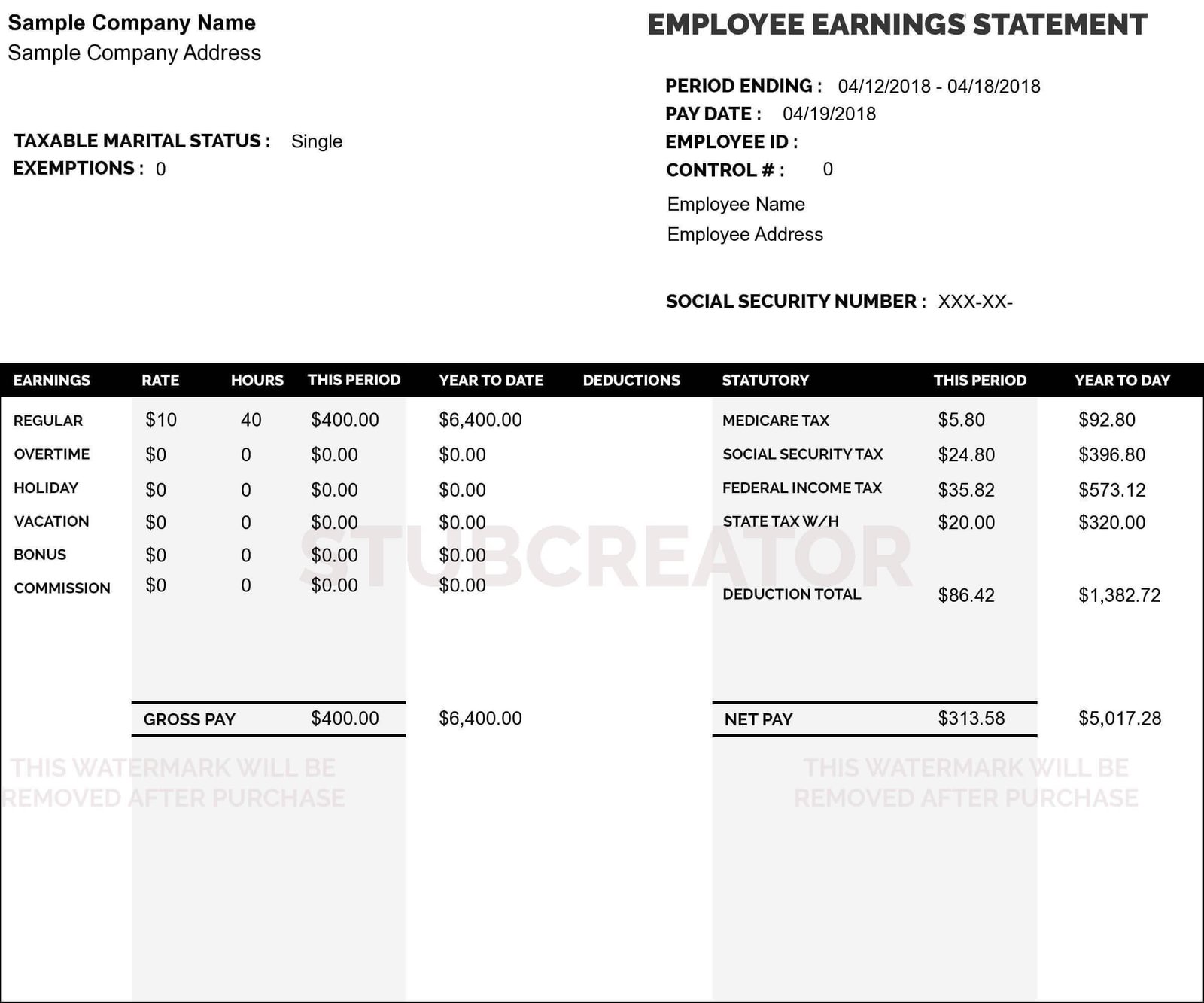
What's Balance Sheet Form?
The balance sheet serves as the foundation for calculating investor rates of return and assessing a company’s capital structure.
Precisely, a balance sheet is a financial statement that indicates what a firm owns and owes and where the business stands within the context of the Business Plan.
Balance sheets can be used in conjunction with other essential financial accounts to perform a basic analysis of the financial position and study financial ratios.
What is the Equation and Formula for the Balance Sheet?
The balance sheet equation is similar to the accounting equation in that assets are on one side, liabilities and shareholder equity are on the other, and both sides balance.
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholder’s Equity
The equation states that a company pays for what it possesses (assets) by borrowing money (liabilities) or taking it from shareholders or investors (equity).
What is the Sequence of Presentation in a Balance Sheet?
Current assets and liabilities must be recorded separately under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Similarly, current Liabilities must be distinguished from long-term liabilities.
Cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenditure are examples of current asset accounts, whereas long-term asset accounts include long-term investments, fixed assets, and intangible assets.
Current liability accounts include long-term debt, interest payable, wages, and pending suppliers’ payments, whereas long-term liabilities include long-term loans, pension fund obligations, and bonds payable.
Accounts for assets will be organized in descending order of maturity, while liabilities will be organized in ascending order. Accounts are classified in decreasing order of priority under shareholder’s equity.
Why is the Balance Sheet Important?
Small business owners may not believe they require balance sheets, yet these financial documents are critical for various reasons.
For a common man, balance sheets may show you what your account receivables are if you provide a service or goods on credit, as well as all of your obligations, giving you a glimpse of how your enterprise is performing.
A balance sheet also provides you with the data you need to compare your company’s Key performance indicators to those of similar businesses.
Balance sheets are also useful in deciding whether to take on more debt to expand operations or lower the interest rate on existing debt.
What role does the Balance Sheet play in Financial Modeling?
This statement is an excellent tool to assess a company’s financial situation. A balance sheet may be used by an analyst to construct a variety of financial ratios that assist in establishing how well a firm is functioning, how liquid or solvent it is, and how efficient it is.
Changes in balance sheet accounts are also utilized in the cash flow statement to compute net cash flow.
A positive change in plant, property, and equipment, for example, is equal to capital expenditure less depreciation expense.
How is the Analysis of the Balance Sheet done?
The balance sheet may be seen separately or in conjunction with other statements, such as the income statement and cash flow statement, to provide a complete picture of a company’s position.
The following are four critical financial success metrics:
- Liquidity is determined by comparing a company’s current assets to its current obligations.
- Examining how a firm is financed reveals its leverage, which in turn reveals the financial risk the company is incurring.
- Combining the income statement and the balance sheet allows one to determine how effectively a firm uses its assets.
- The balance sheet may be used to assess a company’s ability to create returns.
Balance Sheet Questionnaire:
1. Balance Sheet vs Income Statement
The balance sheet and income statement are both key financial statements, but they serve different purposes:
- Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It lists assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity, showing what the company owns and owes.
- Income Statement: Shows a company’s financial performance over some time. It details revenues, expenses, and profits or losses, illustrating how much the company earned and spent.
2. What’s a Balance Sheet?
A balance sheet is a financial statement that summarizes a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time. It provides a snapshot of the company’s financial health, showing what it owns and owes.
3. How to Make a Balance Sheet?
To make a balance sheet:
- List Assets: Organize current and non-current assets, such as cash, accounts receivable, and property.
- List Liabilities: Detail current and long-term liabilities, like accounts payable and loans.
- Calculate Equity: Determine shareholders’ equity by subtracting total liabilities from total assets.
- Format: Ensure the balance sheet equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) is balanced.
4. Balance Sheet Versus Profit and Loss
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific date, detailing assets, liabilities, and equity. The profit and loss (P&L) statement, or income statement, summarizes revenues, expenses, and profits over some time, showing the company’s financial performance. The balance sheet reflects the company’s economic status, while the P&L statement highlights its operational results.
5. How to Create a Balance Sheet in Excel?
How to create a balance sheet in Excel:
- Open Excel: Start a new workbook.
- Set Up Headers: Label columns for “Assets,” “Liabilities,” and “Equity.”
- List Assets: Enter current and non-current assets under the “Assets” section.
- List Liabilities: Enter current and long-term liabilities under the “Liabilities” section.
- Calculate Equity: Deduct total liabilities from total assets to find equity.
- Format: Ensure totals for assets equal the sum of liabilities and equity. Use formulas for calculations.
- Review: Double-check entries for accuracy and balance.
6. What Appears on a Balance Sheet?
A balance sheet displays a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. It shows what the company owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the residual interest of the owners (equity) at a specific point in time.
7. Why is a Balance Sheet Important?
The balance sheet is crucial because it provides a clear snapshot of a company’s financial health at a specific moment, helping stakeholders assess liquidity, solvency, and overall economic stability.