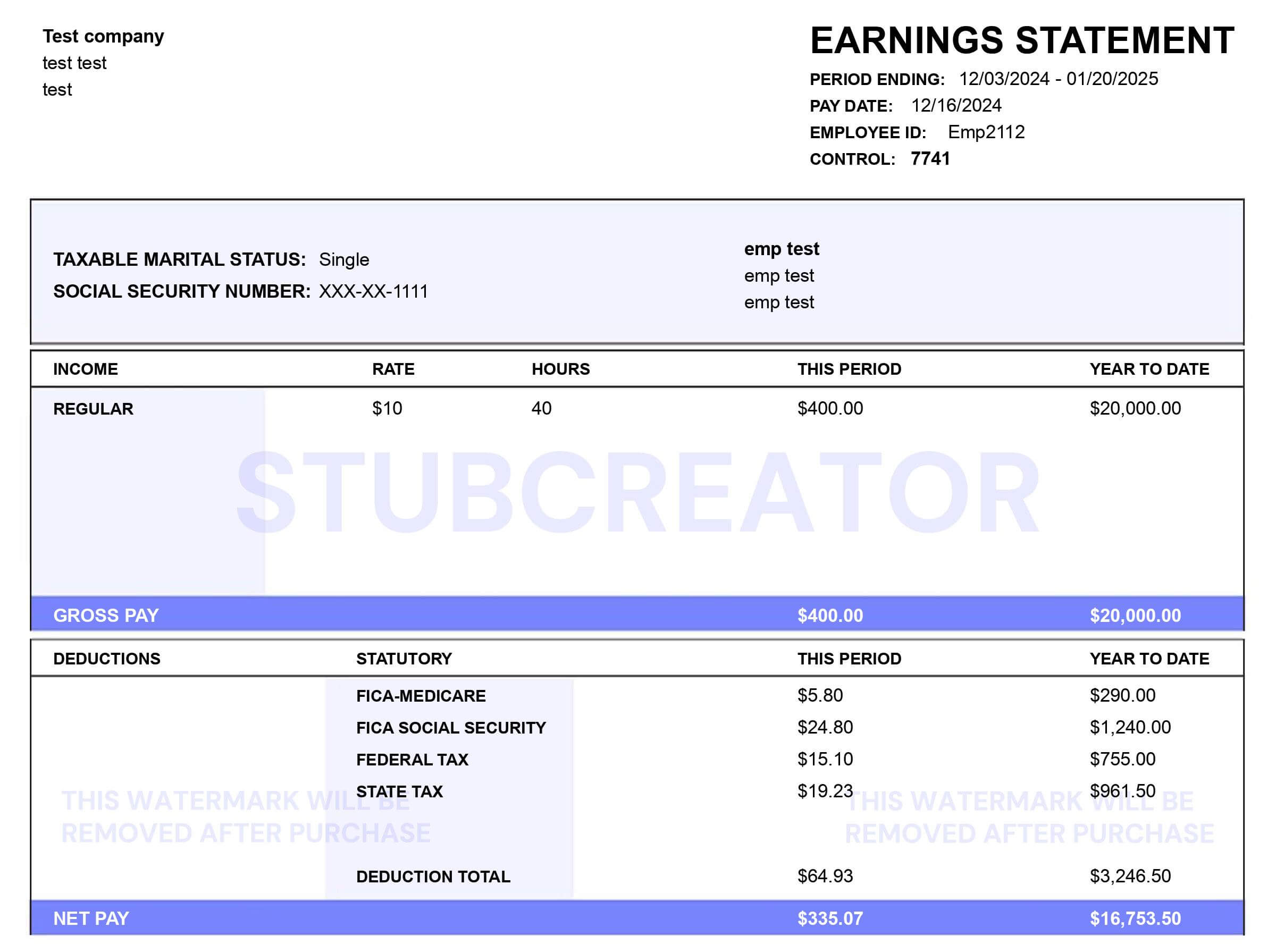
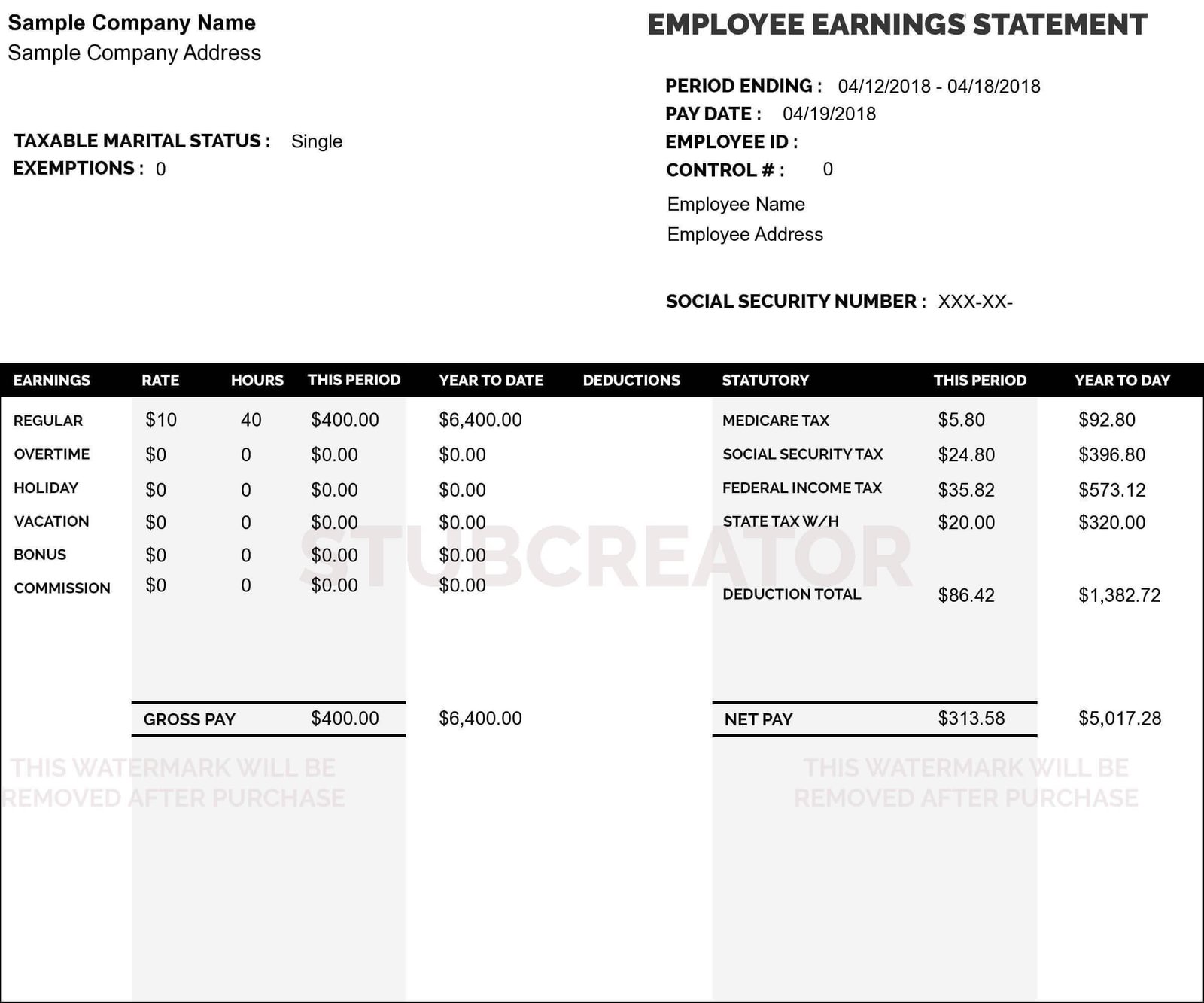
What is a Business Plan Outline?
In your pitch to potential investors, you should outline the objectives of your firm and explain how you plan to turn a profit.
It also acts as a road map for your firm, keeping it on course and ensuring that activities expand and change to fulfil the objectives set forward in your strategy.
A business plan can be a live document that adapts as conditions evolve, but it should always reflect the main objectives of your company.
What Makes a Business Plan Necessary?
Launching a new business can be stressful. Having a plan in place will greatly limit the impact those difficulties will have on your company. Writing a strong business plan is a crucial step in becoming ready for whatever problems your startup may have.
You can more clearly realize what needs to be done to achieve your goals by writing a business strategy. Your completed company plan will serve as a reminder of these objectives. You can use it as a useful tool to help you keep focused and on course.
Different Business Plan Types
Simple and traditional business strategies are the two primary categories.
Traditional business plans are extensive, in-depth documents that outline both short-term and long-term goals.
A simple business plan, in contrast, concentrates on a few key metrics in short detail to quickly exchange information with investors.
Simple Business Plan
Ash Maurya, a specialist in business models, has created a straightforward company strategy known as a “lean canvas.” The model, which was created in 2010, is still among the most frequently imitated formats for company plans.
The nine areas of a lean canvas contain high-value data and metrics that will appeal to investors in each segment. This one-page lean business strategy frequently includes the following information:
- Problem
- Solution
- important metrics
- original suggestion
- improper advantage
- Channels
- customer goals
- structure of costs
- income sources
Traditional Business Plan
Traditional plans are complex documents that can be 30 or 40 pages long. They serve as a roadmap for a new company, outlining its development from its founding until it becomes established several years later.
Traditional business plans cover the following topics:
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Products and services
- Market analysis
- Management team
- Financial plan
- Operational plan
- Appendices
What are a business plan’s three key goals?
It’s essential to consider why a business plan is being created before you begin to compose one.
The following are the top three reasons for creating a business plan:
Decide on a business strategy
Establishing your future ambitions is the main goal of a business strategy.
These strategies should outline the activities your business will take to achieve each objective or goal.
You can choose your business by focusing on and pursuing growth by developing a path to your goals.
Obtain funds
Banks, private investors, and other lenders often require a thorough business plan before investing in your company.
Investors are interested in how you run your company, your projected income and expenses, and, most crucially, how they will get a return on their investment.
Pull in executives
You’ll probably need to expand your team with executives as your company grows.
A business plan can help you find executive talent and evaluate whether they are a suitable fit for your organization.
Business Plans Questionnaire:
1. What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, market analysis, and financial projections. It serves as a roadmap for running the business and securing funding.
2. Why is a Business Plan Essential?
A business plan is crucial because it provides direction for your business, helps attract investors or lenders, and serves as a tool for managing and growing the business effectively.
3. What Does a Business Plan Include?
A business plan typically includes an executive summary, company description, market analysis, organizational structure, product or service offerings, marketing strategy, operational plan, and financial projections.
4. How Do You Make a Business Plan?
To create a business plan, follow these steps:
- Define your business idea and objectives.
- Conduct market research.
- Outline your business model and strategy.
- Develop a marketing and sales plan.
- Create financial projections and budgets.
- Write the plan in a clear, structured format.
5. What is a Business Model Canvas?
A business model canvas is a visual tool that outlines a business’s key components, including value propositions, customer segments, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, essential resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure.
6. How Can I Find a Sample Business Plan for a Small Business?
You can find sample business plans online through various business plan websites, government resources, or business books. These samples provide templates and examples to guide you in creating your own plan.
7. How Do I Create a Business Plan Template?
To create a business plan template, start by outlining the main sections of a business plan. Use headings and subheadings to organize content, and provide prompts or questions to help you fill in details for each section.
8. What is the Step-by-Step Process for Making a Business Plan?
- Research and gather information about your industry and market.
- Define your business concept and objectives.
- Develop a detailed business strategy.
- Create a financial plan and projections.
- Write the business plan document, starting with an executive summary.
- Review and revise the plan as needed.